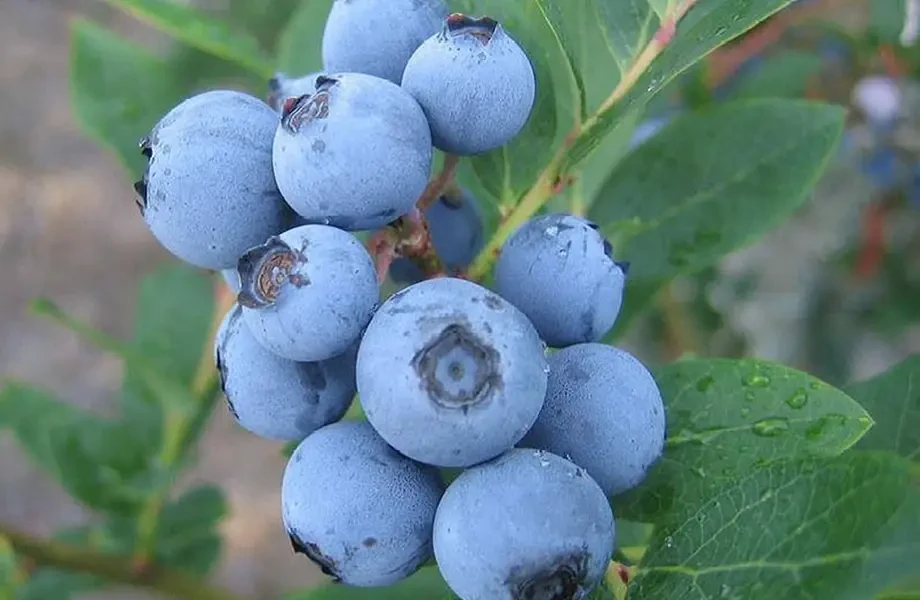
Rabbiteye blueberries (Vaccinium virgatum), although historically appreciated for their hardiness and climate adaptability, are now considered inferior to more recent types, such as Southern Highbush and Northern Highbush, for several reasons related to fruit quality and modern market demands.
Nevertheless, they remain interesting for their health and nutritional properties, as explained by Stefano and Silvia, producers of organic and biodynamic blueberries in the province of Sondrio (Italy).
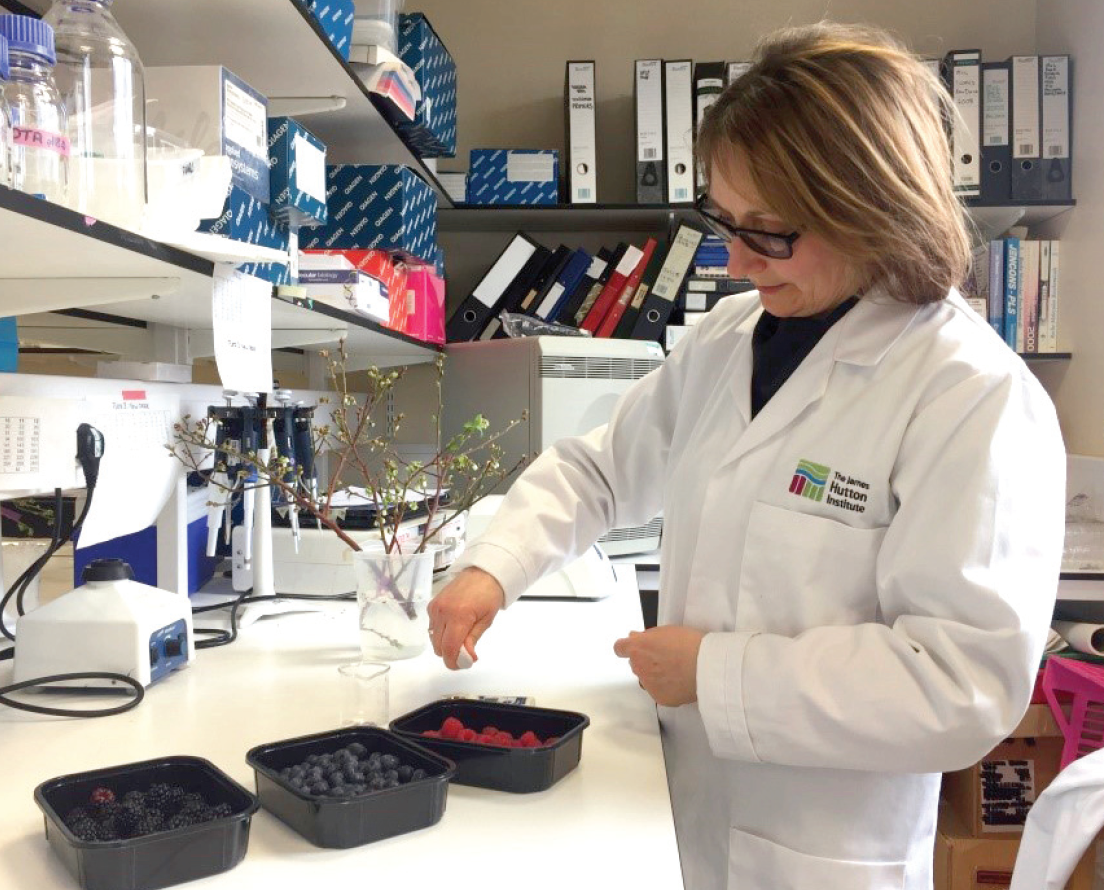
"In a study conducted by the University of Milan, the six varieties of blueberries we cultivate on our farm were compared, and the results show that the late-ripening rabbiteye varieties (Ochlockonee and Overtime) have greater antioxidant power than the classic ones."
 Stefano and Silvia (Alpes Agia)
Stefano and Silvia (Alpes Agia)
This study, published in Agronomy, compares six blueberry genotypes (three tetraploids of Vaccinium corymbosum and three hexaploids of Vaccinium virgatum), cultivated in the Italian Alps, analyzing the chemical profile and antioxidant potential.
Through metabolomic and ionic analyses, researchers identified significant variations among the genotypes, with Ochlockonee and Overtime showing the highest levels of anthocyanins, phenols, and antioxidant activity.
The genotype significantly influences the antioxidant properties of blueberries. This is mainly due to genetic variations that determine the concentration and composition of bioactive compounds such as anthocyanins, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. These compounds are crucial for the antioxidant activity of blueberries and therefore their ability to promote health.
The analysis particularly highlights the importance of the quality of phenolic compounds, rather than their total quantity, in influencing antioxidant effectiveness. The results suggest a greater antioxidant potential for rabbiteye blueberries compared to highbush blueberries.
 The quality of phenolic compounds determines the effectiveness of antioxidants more than their quantity
The quality of phenolic compounds determines the effectiveness of antioxidants more than their quantity
The relationship between the quantity and quality of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity is complex, but studies suggest that the quality of phenolic compounds is more important than their quantity in determining antioxidant effectiveness. This concept is clearly evident in the analysis of the different blueberry genotypes in this study.
Here are some key points explaining this relationship:
- Quantity vs. Quality:
- Some genotypes, such as Last Call and Legacy, had a higher number of metabolites, including organic acids and sugars. However, these genotypes showed lower antioxidant activity than others.
- Conversely, genotypes such as Overtime and Ochlockonee, while not having the highest quantity of metabolites, exhibited the highest levels of antioxidant activity, suggesting that the composition and quality of phenolic compounds are crucial.
- Specific Composition of Phenols:
- The specific composition of phenolic compounds, particularly the presence of anthocyanins and other flavonoids, is a determining factor for antioxidant activity.
- The study found that Overtime had the highest phenolic content, followed by Ochlockonee, both with high antioxidant activity. In general, rabbiteye blueberries show greater antioxidant potential compared to highbush blueberries, indicating that antioxidant effectiveness depends more on the composition and quality of bioactive compounds than on their total concentration.
- Antioxidant Effectiveness:
- Antioxidant effectiveness depends on the ability of phenolic compounds to neutralize free radicals. Genotypes with a superior phenolic profile, such as Overtime and Ochlockonee, are more efficient in this neutralization than those with a greater quantity but lower quality of compounds.
- Key Metabolites:
- Metabolites such as citric acid, isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside, and 2-hydroxycinnamic acid have been identified as important for oxidative stress defense and genotype differentiation. These compounds not only contribute to the fruit's taste but also to its antioxidant capacity.
- Multivariate Analysis:
- Multivariate analysis confirmed that genotypes with higher quality phenolic compounds cluster distinctly and have greater antioxidant activity.
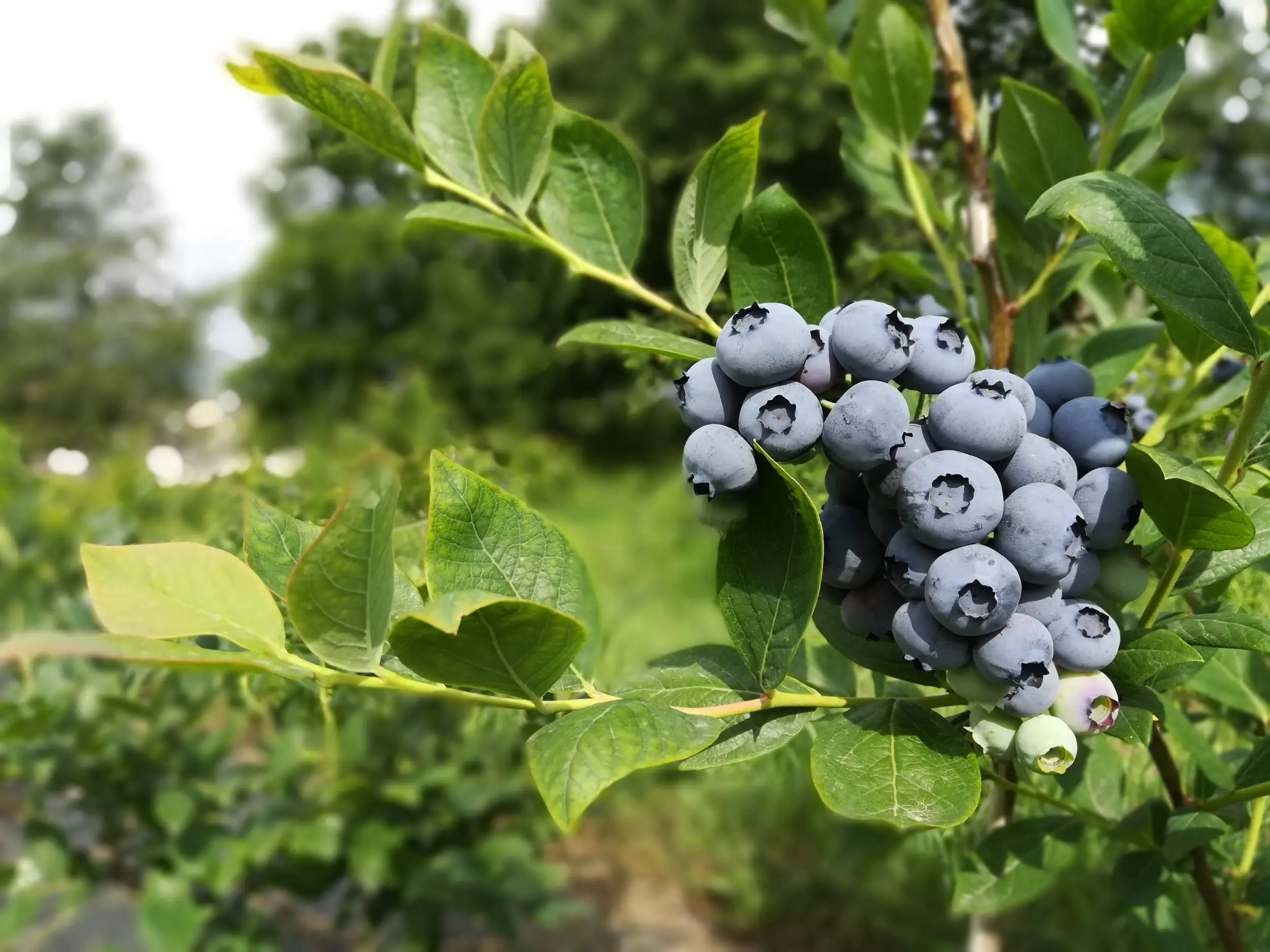 Blueberries produced by Alpes Agia in the province of Sondrio (Italy)
Blueberries produced by Alpes Agia in the province of Sondrio (Italy)
The relationship between the quantity and quality of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity indicates that quality, meaning the specific composition of phenols, is the most determining factor for the antioxidant effectiveness of blueberries. This suggests that selecting specific genotypes based on their phenolic composition is essential to maximizing health benefits.
Rabbiteye blueberries are part of the production calendar of Alpes Agia farm to extend the harvest season until August. Stefano and Silvia, two agronomists who have been managing production for 13 years, add: "Our farm covers an area of about 2 hectares, mostly cultivated with blueberries and a small area with vegetables. From the beginning, we chose to produce organically, and for five years, we have also embraced biodynamic agriculture."
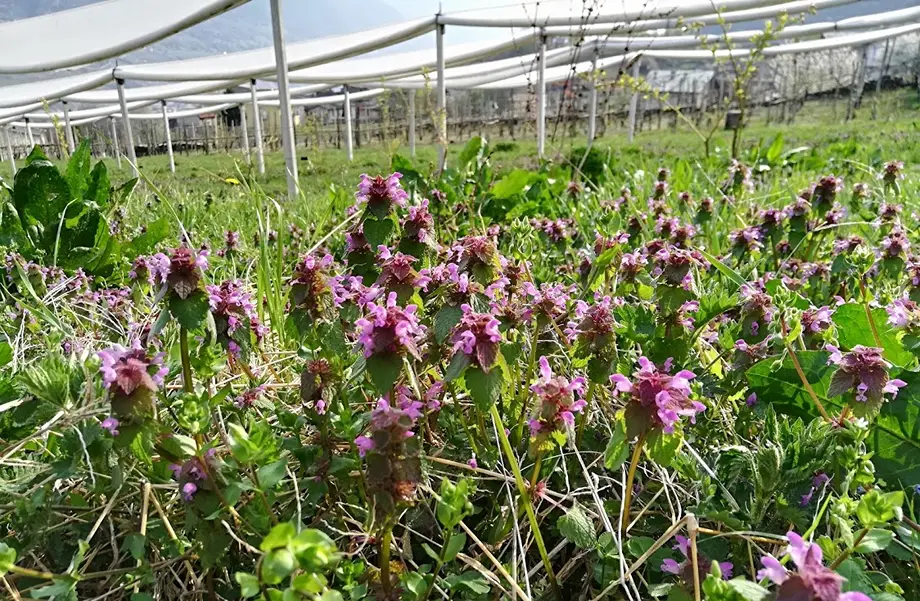 Various flower species contributing to the biodiversity of Alpes Agia
Various flower species contributing to the biodiversity of Alpes Agia
Regarding certifications: "To date, in addition to organic certification, we are also BIOSUISSE and DEMETER certified. Furthermore, we are part of the BIODISTRETTO DELLA VALTELLINA (we are among the founding members)."
The commercialization of blueberries "is carried out through APOFRUIT while vegetables are delivered to local NATURA Sì stores. Thanks to collaboration with a social cooperative in the valley, part of the blueberry production is transformed into organic nectars and jams."