Blueberry farming plays a central role in the agriculture of British Columbia, Canada, contributing millions of dollars to the economy every year.
However, a significant threat looms over these plantations: the blueberry scorch virus (BIScV), transmitted by aphids.
This virus can severely compromise the health and productivity of blueberries, causing substantial economic losses for farmers.
But now, thanks to artificial intelligence (AI) and drone technology, an innovative solution promises to transform the management of this disease.
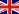
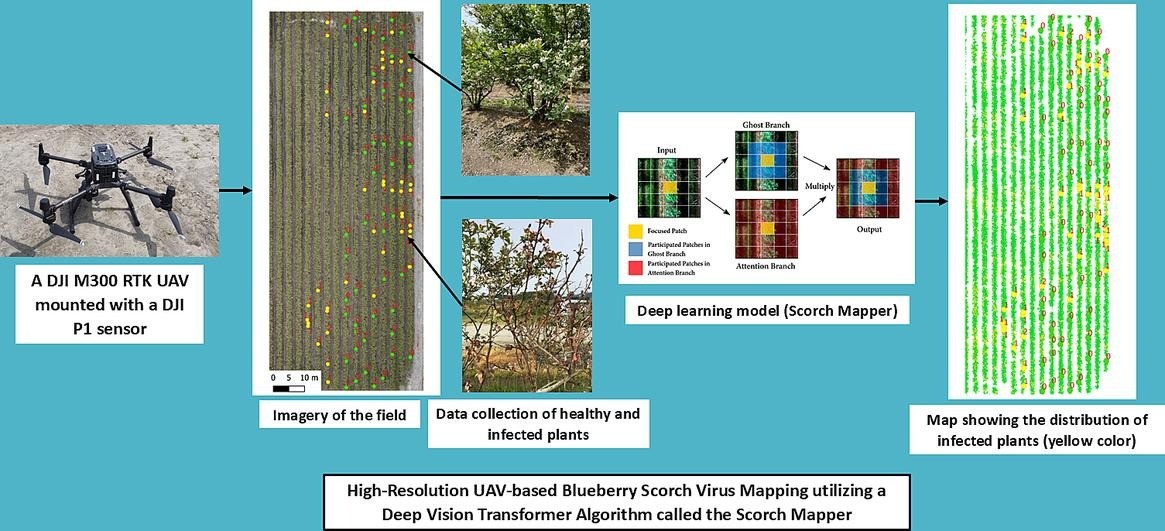 Figure 1. High-Resolution UAV-based Blueberry Scorch Virus Mapping utilizing a Deep Vision Transformer Algorithm called the Scorch Mapper.
Figure 1. High-Resolution UAV-based Blueberry Scorch Virus Mapping utilizing a Deep Vision Transformer Algorithm called the Scorch Mapper.
The problem of blueberry scorch virus
BIScV is one of the most devastating diseases for blueberries in Canada, with symptoms such as leaf chlorosis, necrosis, and bush dieback.
In some cases, infections reduce yields by over 85% within a few years, forcing farmers to replant entire fields.
Manual detection of the disease is time-consuming, expensive, and prone to human error, making the adoption of faster, more accurate, and scalable methods urgent.
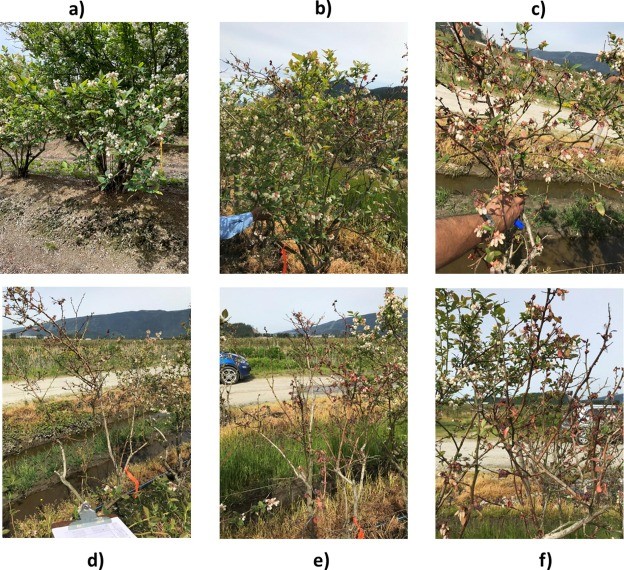 Figure 2. Examples of blueberry plants that were visually assessed.
Figure 2. Examples of blueberry plants that were visually assessed.
An innovative solution: the "Scorch Mapper"
Recent research has introduced the "Scorch Mapper," a deep learning algorithm designed to map BIScV infections using high-resolution imagery captured by drones (UAVs).
This tool combines two advanced technologies: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViT), to provide detailed maps that distinguish healthy plants from infected ones.
How the "Scorch Mapper" works
- High-Resolution Data Collection: Drones equipped with advanced sensors fly over the fields, capturing detailed images.
- Intelligent Analysis: The algorithm processes the images, using CNNs to identify local features (e.g., leaf texture and color) and ViTs to detect broader contextual patterns.
- Accurate Maps: The processed data generates highly precise maps that help farmers quickly identify infected areas.
 Figure 3. The structure of the “Scorch Mapper”.
Figure 3. The structure of the “Scorch Mapper”.
Promising results
Tested on two blueberry fields in Pitt Meadows, British Columbia, the "Scorch Mapper" demonstrated extraordinary effectiveness:
- Superior Accuracy: Achieved 70.71% accuracy in one field and 78.15% in the other, outperforming advanced models like ResNet and Swin Transformer.
- High F1 Scores: Improved precision in identifying infected plants by 5-13% compared to competing algorithms.
- Scalability: The model proved robust and transferable, performing well across different fields without the need for retraining.
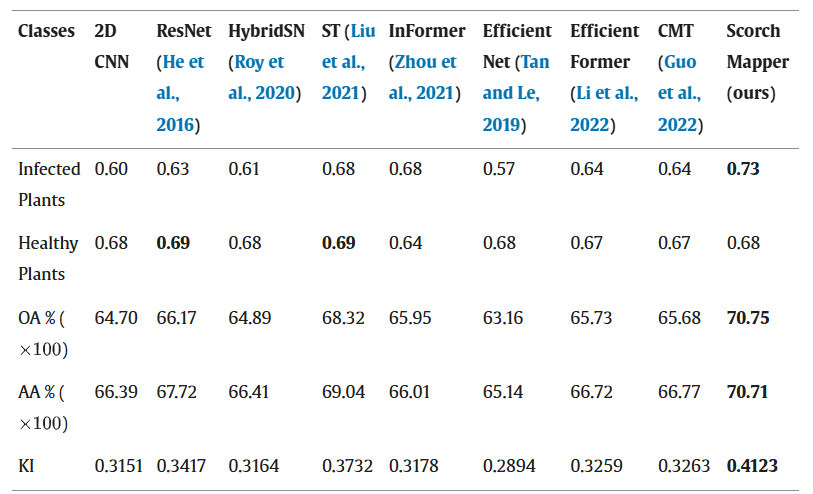 Table 1. The blueberry scorch disease classification results of the developed convolutional neural networks and vision transformer algorithms.
Table 1. The blueberry scorch disease classification results of the developed convolutional neural networks and vision transformer algorithms.
Practical benefits for farmers
The introduction of the "Scorch Mapper" offers tangible benefits to farmers:
- Cost and Labor Savings: Automated detection significantly reduces the need for manual inspections.
- Improved Crop Health: Early diagnosis allows quick action, preventing the spread of the virus.
- Scalable Monitoring: Ideal for large-scale operations due to its ability to generalize across different fields.
- Informed Decision-Making: Precise maps enable better disease management and planning.
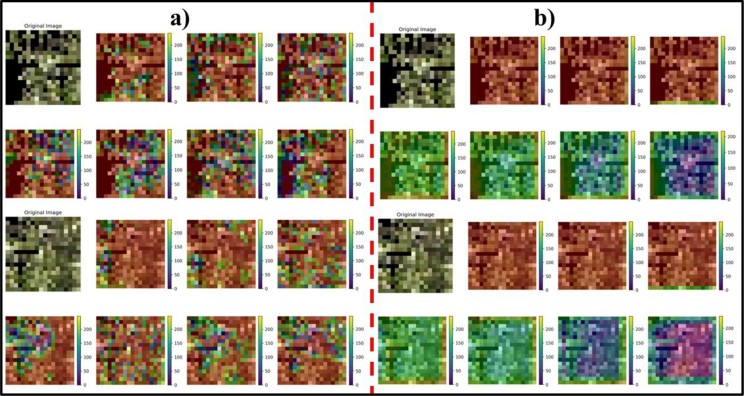 Figure 4. A few selected output feature maps of - a - the attention module and - b - the last convolutional layer in the developed Scorch Mapper architecture.
Figure 4. A few selected output feature maps of - a - the attention module and - b - the last convolutional layer in the developed Scorch Mapper architecture.
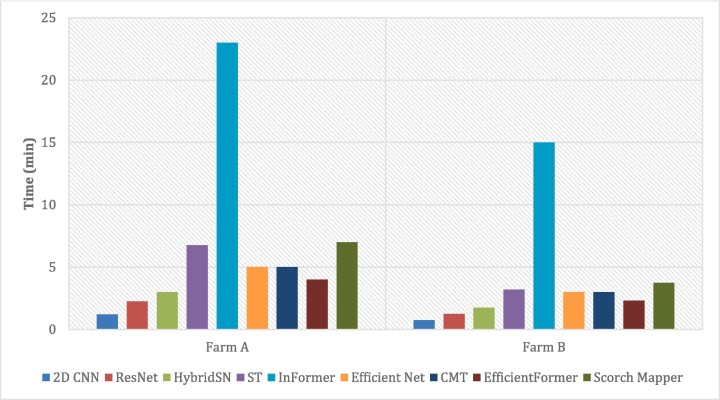 Table 2. The computational costs of the developed convolutional neural networks and vision transformer algorithms in terms of training time for blueberry scorch disease datasets from Field A and Field B.
Table 2. The computational costs of the developed convolutional neural networks and vision transformer algorithms in terms of training time for blueberry scorch disease datasets from Field A and Field B.
Challenges and future prospects
Despite its promising results, the "Scorch Mapper" has some limitations:
- Dependence on Small Datasets: This can lead to overfitting, reducing effectiveness in new conditions.
- Difficulty in Early Detection: Mild infections (severity level 1) are hard to distinguish from other issues like nutrient deficiencies.
- Costs and Complexity: High computational requirements and technical expertise make adoption less accessible for smaller farms.
Nevertheless, the "Scorch Mapper" represents a significant step toward a future where AI enhances agricultural sustainability and efficiency.
With further developments, such as integrating multispectral imaging, this technology could become even more precise and effective.
A new era for blueberries
The blueberry industry is entering a new era.
Technologies like the "Scorch Mapper" not only protect crops but also ensure the economic sustainability of farmers.
This is the perfect example of precision agriculture, where artificial intelligence is used to solve critical challenges and secure a prosperous future for the agricultural sector.
Source: AI in Agrocolture
Figures and tables source: Jamali et al., 2025
Reference FMach: openpub.fmach.it