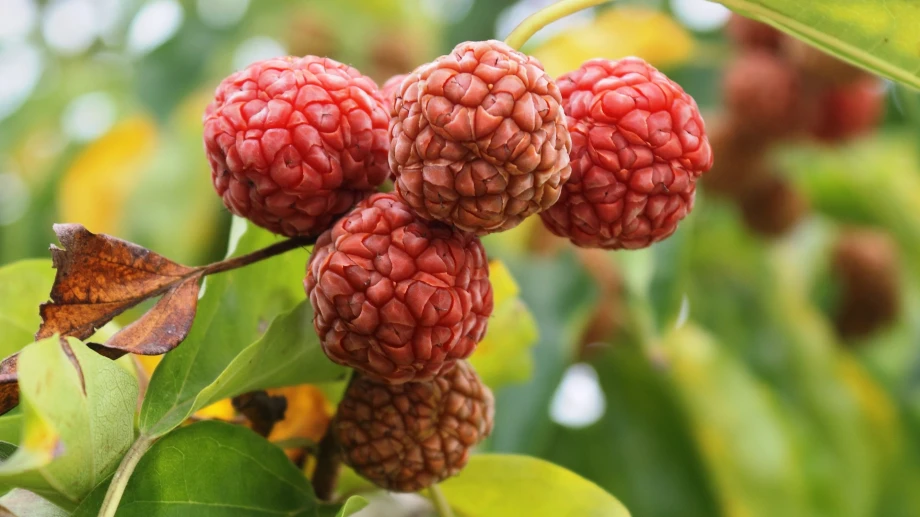
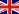
The melon berry (Maclura tricuspidata) is native to the Himalayan highlands in China and Nepal. The fruit resembles a giant raspberry on a tree and is edible and delicious. It is also known as Mandarin Melon Berry, Che, Chinese bramble berry, kudrang. Botanically, it is a member of the Moraceae family along with several species of the genera Artocarpus (breadfruit), Ficus (fig) and Morus (mulberry).
The melon berry has a sweet and juicy taste, reminiscent of a mix between melon and raspberry. Its rarity and exotic charm make it an intriguing addition to diets and menus, offering a new and interesting taste experience.
Also known as Mandarin Melon Berry or Che, it is an ornamental tree that, when grown from seed or cuttings on its own roots, grows into a large shrub reaching just about 1.8 meters (6 feet) in height and width. However, when grafted onto Osage Orange rootstocks, the trees can eventually reach up to 6 meters (20 feet) in height.
Melon Berry Characteristics
The melon berry has a spherical shape and a bright red color when ripe. The fruit is relatively small, similar to a grape, but its flesh is soft and very juicy. Its texture, similar to that of a strawberry, makes it perfect for fresh consumption or use in a variety of culinary preparations. The fresh fruit is highly perishable and should be consumed within a few days of harvest.
The Flavor
Before reaching full maturity, the melon berry has an unpleasant taste, but when fully ripe it has a flavor that is often described as sweet, with floral notes, resembling other fruits. Here are some comparisons:
Watermelon: When the fruit is soft, it has a flavor similar to watermelon, sweet and juicy.
Pumpkin and Mango: Some people describe the flavor as a cross between pumpkin and mango, suggesting a sweet and slightly earthy taste profile.
Mulberry and Lychee: The fruit is also compared to mulberry and lychee, both known for their sweet and slightly tangy flavors.
 Photo: IDSeeds
Photo: IDSeeds
How to Consume Melon Berry
The melon berry can be consumed in various ways, offering a wide range of versatility in the kitchen. Fresh, the fruit is delicious as a healthy snack or added to fruit salads for an exotic touch. It can be used to make juices, smoothies, and shakes, thanks to its sweet flavor and juicy texture.
Additionally, the melon berry is excellent for making jams and preserves, which can be used as toppings for bread, pancakes, and desserts. Its pulp can be turned into sweet sauces to accompany white meats or fish, offering an interesting contrast of flavors. Desserts based on melon berry, such as cakes and ice creams, are also gaining popularity thanks to their originality and unique taste.
Besides the fruit, the Melon Berry is also used as a flavoring in e-cigarette liquids, where it is described as having a fresh and fruity taste with notes of watermelon, strawberry, and ice.
Cultivation and Availability
Maclura tricuspidata, also known as Chinese Mulberry, can be cultivated in various regions thanks to its ability to adapt to different climates and soil conditions.
Here are some details on where it can be grown:
- Native Habitat: The tree is native to East Asia, particularly in the Shantung and Kiangson provinces in China and the foothills of the Nepalese Himalayas.
- Climate Zones: It can grow well in temperate zones with mild winters and hot summers.
- Subtropical Regions: The tree can also thrive in subtropical regions, which have milder winters and more consistent temperatures.
- Specific Locations: It has been introduced to France, England, and the United States, where it can be grown in regions with suitable climates.
- Florida: In Florida, it can be grown in the northern and central regions, where it is suitable for cultivation and can tolerate drought and cold temperatures.
- Other Regions: The tree can be grown in other warm temperate regions of the globe, including southern Europe.
While in nature the Melon Berry has both male and female plants, the plants offered for sale are self-fertile female selections, so only one plant is needed for fruiting. The seeds available will naturally produce both male and female plants.
Overall, Maclura tricuspidata is a versatile tree that can be cultivated in a variety of climates and regions, making it a popular choice for gardeners and farmers.
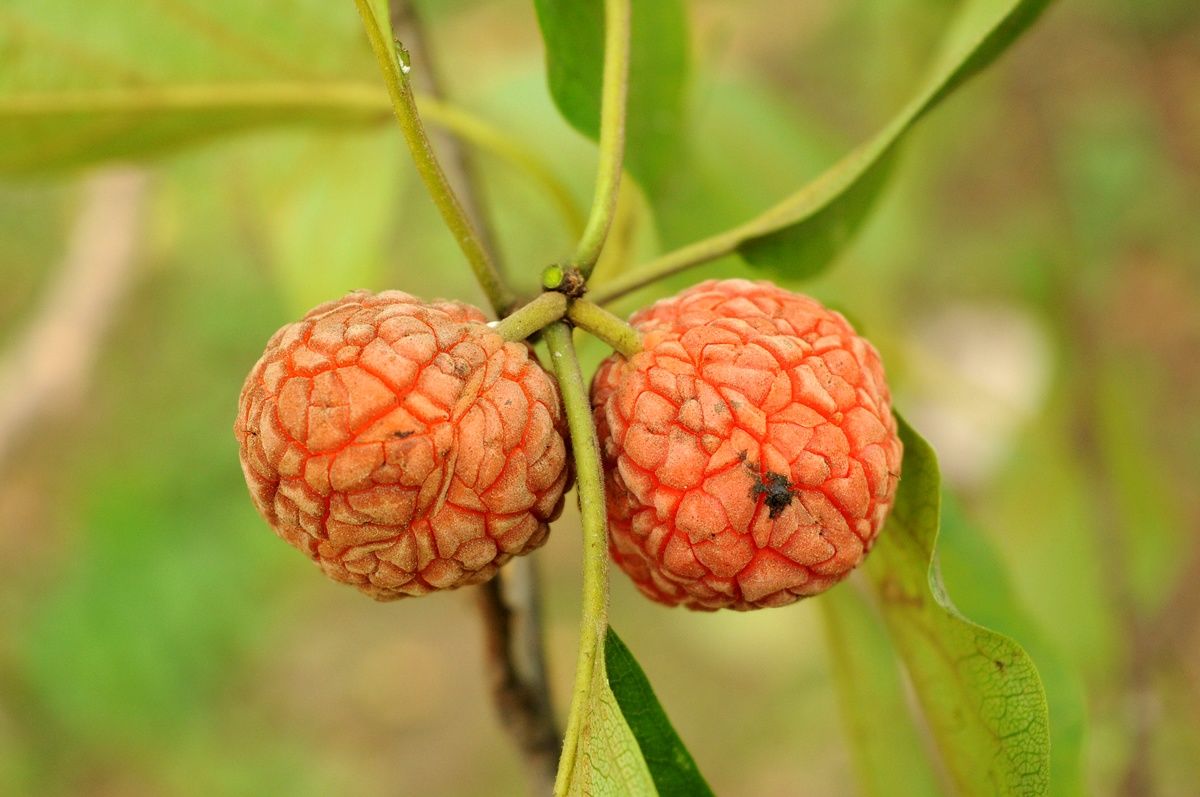 Photo: KEW
Photo: KEW
Health Benefits
Maclura tricuspidata is a plant that has attracted the attention of the scientific community for its numerous health properties. Its ability to combat free radicals, inhibit tumor growth, protect nerve cells, and act against pathogenic bacteria makes it a subject of great interest for future therapeutic applications. Recent studies have highlighted the following benefits:
- High biological activity, such as antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and anticancer activities.
- Abundant amount of morin, a powerful antioxidant compound with chelating, antimutagenic, anti-inflammatory, antineoplastic, and cardioprotective properties.
- High content of resveratrol, a compound found in some plant species, with preventive effects for neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's.
- Powerful aid in the treatment of obesity, able to regulate carbohydrate/lipid/energy metabolism by inhibiting enzymes related to this condition.